International money transfers were once a hassle. Payments would disappear, end up in the wrong account, or bounce back unexpectedly. Customers lost time, money, and even trust.
That was before IBAN.
To understand why the International Bank Account Number (IBAN) is so important today, let’s rewind a little. Because IBAN didn’t just appear overnight—it was built out of necessity. And its evolution tells us why it’s become one of the most critical elements in modern cross-border banking.
Before IBAN: The Chaos of Cross-Border Transfers
In the earlier days of international trade, bank transfers between nations were far from seamless. Account numbers within nations were as varied as they were anywhere else—six digits here, twenty there. There was no standard format. Routing depended a great deal on keying, which introduced mistakes and pauses.
If a company in France wanted to pay a supplier in Portugal, they had to ensure the bank name, branch code, and account number were correct—down to the letter. And even then, something could go awry. If one of the digits was misplaced, the money could disappear into the system, sometimes for weeks on end.
Errors weren’t simply the norm—they cost money. Failed payments were likely to incur penalty fees, delayed reconciliations, and broken business relationships.
What Is IBAN?
IBAN stands for International Bank Account Number. It’s a unique, standardized code that identifies a specific bank account across national borders. It contains all the information needed to route an international transfer correctly.
Unlike traditional account numbers, which are often usable only within their home country, an IBAN is globally readable and verifiable.
It doesn’t replace your account number—it expands it for international use.
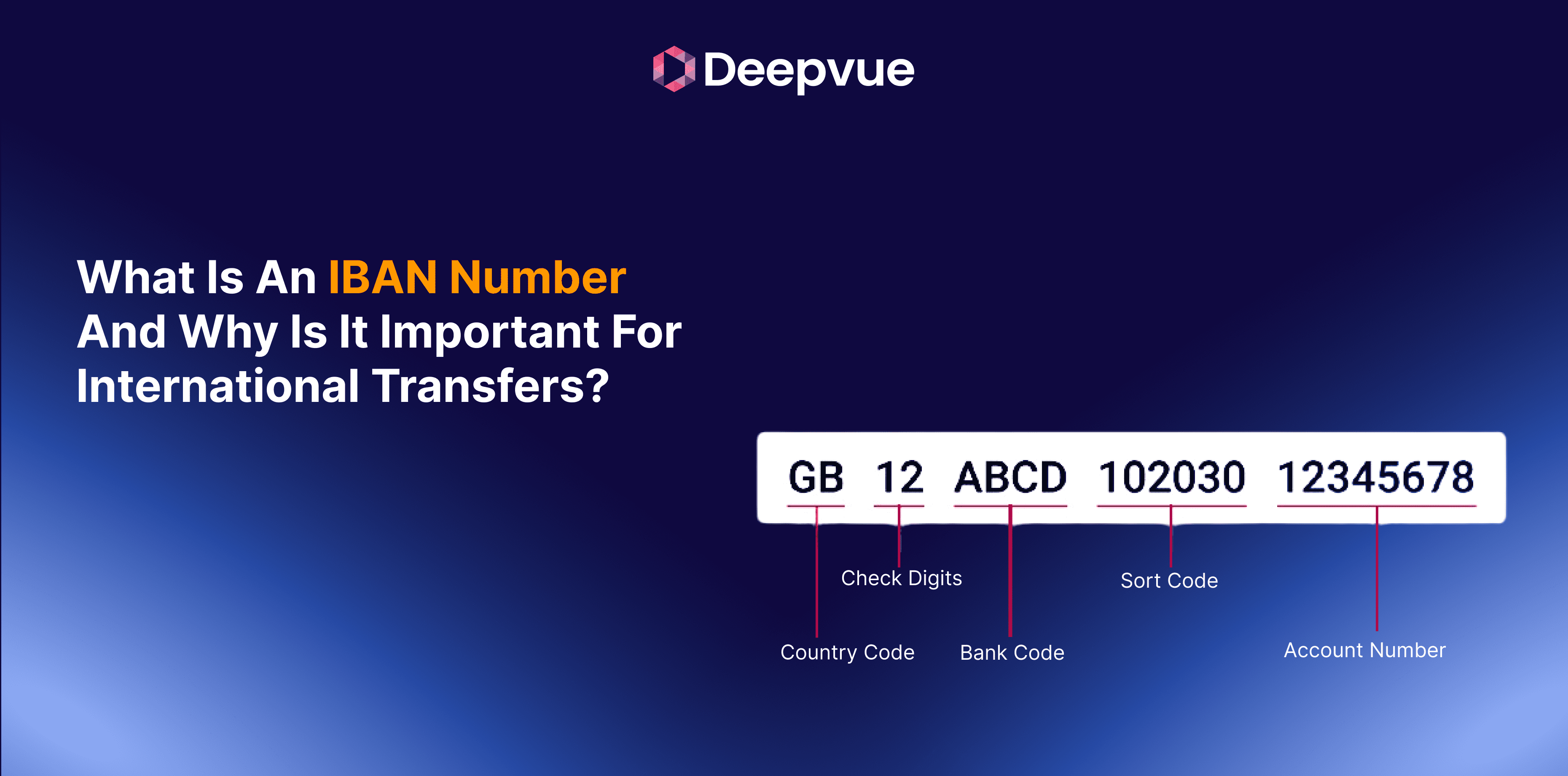
The Structure of IBAN: What’s Inside the Number?
An IBAN can be up to 34 alphanumeric characters, though the length varies by country. Every IBAN contains:
- Country Code: 2 letters (e.g., DE for Germany)
- Check Digits: 2 numbers for error detection
- Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN): Bank-specific details, including branch code and account number
Example:
GB29 NWBK 6016 1331 9268 19
Where:
- GB = United Kingdom
- 29 = Check digits
- NWBK 6016 1331 9268 19 = Sort code + Account number
The structure isn’t just for show—it’s actually for checking errors. Banks employ the check digits to check whether an IBAN is valid before they process the transfer.
The Power of IBAN in Practice
Let’s look at a practical example.
An IT consultant in Italy is being paid by a client in Germany. Without IBAN:
- The client would have to manually enter the bank name, branch, account number, and pray that it’s all correct.
- A single typo might result in an improperly routed payment or outright failure.
With IBAN:
- The consultant provides a single number.
- The client’s bank verifies it in real-time.
- The funds go straight into the correct account—no confusion, no mistake.
IBAN eliminates guesswork. It’s speedy, neat, and traceable.
IBAN vs SWIFT Code: What’s the Difference?
This is where confusion normally happens.
IBAN identifies a precise account.
SWIFT (or BIC) identifies the bank or financial institution.
Think of IBAN as the house address, and SWIFT as the name of the building. Both are often used together in international payments.
| Feature | IBAN | SWIFT/BIC |
| Purpose | Identifies an account | Identifies a bank |
| Scope | Country-specific + global | Global |
| Format | Alphanumeric (up to 34 chars) | 8 or 11 characters |
IBAN and India: What You Should Know
India doesn’t use IBAN domestically—but it interacts with IBAN every day.
If you’re in India:
- Sending money to an IBAN country? You’ll need the recipient’s IBAN and SWIFT code.
- Receiving money from an IBAN country? The sender will use your bank’s SWIFT code and your regular Indian account number.
Indian exporters, freelancers, and remote workers often deal with IBAN when getting paid from Europe or the Middle East.
Tools for IBAN Validation
Banks and fintech platforms now provide IBAN validation tools that verify:
- IBAN length
- Proper usage of country code
- Correct check digits
These tools eliminate invalid transfers and are both time- and cost-saving.
A few platforms even pre-validate IBANs at the time of onboarding or prior to processing payouts, allowing businesses to scale cross-border payments effectively.
Common Issues to Avoid with IBAN
- Manual errors: Typing one wrong character breaks the entire validation.
- Using domestic account numbers for international payments (won’t work).
- Incorrect SWIFT–IBAN pairing: If the SWIFT code doesn’t match the IBAN’s bank, the transaction may be flagged or rejected.
Tip: Always cross-verify with the recipient and utilize IBAN validation tools prior to remitting money.
Benefits of IBAN for Businesses and Individuals
- Faster payments: Transactions land faster when routing is precise.
- Fewer chargebacks: Reduce the time and cost of failed transfers.
- Global readiness: Easier to work with partners and clients abroad.
- Improved reconciliation: IBAN-based payments are traceable and easy to match with invoices.
IBAN in the Future: Will It Go Fully Global?
IBAN adoption is steadily growing.
Fintech platforms are increasingly building IBAN support into APIs. Global payment gateways are encouraging customers to switch to IBAN-based formats. And with ISO 20022 and SEPA in the lead, global financial messaging is becoming standardized.
There is likely to be a strong possibility that other non-European countries (like India or the US) will implement IBAN-style systems in the future to reduce friction for payments and align with international systems.
The direction is unmistakable: the globe is heading towards universal account identifiers—and IBAN is leading the charge.
Conclusion: From Chaos to Clarity
The IBAN has revolutionized the way the world transfers money.
It transformed what was previously a clunky, mistake-ridden system into a seamless, reliable process. If you’re an entrepreneur doing business with foreign customers or simply someone remitting money to relatives overseas, knowing IBAN puts you ahead.
It’s not just a figure—it’s a bridge over borders.
FAQ
Is an IBAN the same as a bank account number?
No. An IBAN includes your account number plus extra characters like country code and check digits for international use.
Do I need an IBAN to send money abroad?
If the recipient’s country uses IBAN, then yes—most international payments now require it.
Can I use IBAN for domestic transfers?
Yes, in some countries (especially in Europe), IBANs are used even for local transfers.
Is IBAN used in India?
India doesn’t issue IBANs but requires them for sending payments to IBAN-using countries.
Is it safe to share my IBAN?
Yes. Just like a regular bank account number, it’s safe to share for receiving payments.